Ground Source Heat Pumps: Are They Worth the Fuss?

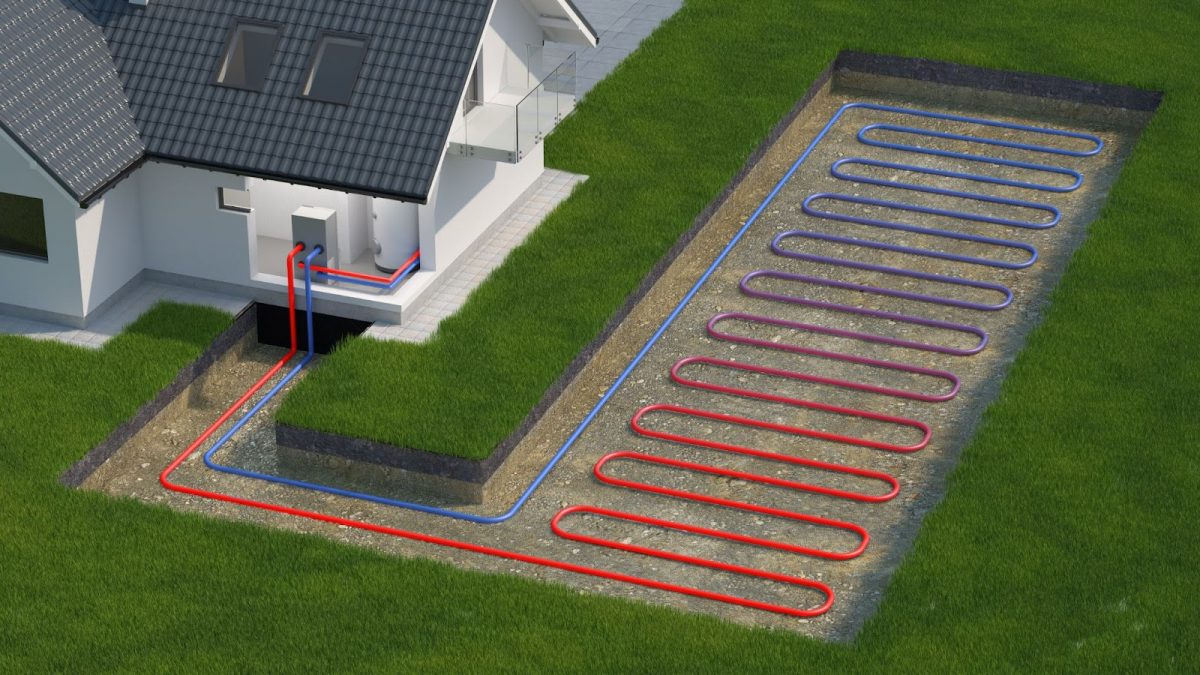
Ground source heat pumps (GSHPs) are an exceptional technical marvel. By using the ground, these systems can create a source of heating and cooling for your home or business that’s reliable, efficient and good-looking. Below, we’ll discuss how ground source heat pumps work along with some pros and cons of choosing it as your primary energy source.
What Is a Ground Source Heat Pump?
Also called a geothermal heat pump, a ground source heat pump is a renewable energy solution that’s highly energy efficient. There’s an increasing acceptance of this type of heat pump on both the residential and commercial sides of the market.
GSHPs are used to heat and cool buildings as well as heat water. They concentrate heat already present in the ground instead of producing heat by burning fossil fuels.
How Does It Work?
A ground source heat pump absorbs the heat from the ground. This heat is then transferred into buildings, supplying hot water and heating while using less energy.
Ground source heat pumps run on electricity. They utilise a system of pipes known as a ground loop, which may be vertically or horizontally installed underground.
The GSHP absorbs ground heat using a fluid or refrigerant, which passes through the ground loop. Electricity is used to compress the fluid and raise its temperature. Afterwards, the heat is transferred to an exchanger and distributed to your heating system.
In return for every kW of electrical energy used, geothermal heat pumps produce around 4 kWh of usable heat, resulting in a 400% efficiency. Thus, your carbon footprint is reduced, and you save money on your energy bills each month.
Heat Pumps in the UK
In the UK, 85% of all heating systems are gas-powered, making the country the largest boiler market in Europe. In contrast, heat pumps only account for 2% of UK heating systems. Currently, air-source heat pumps (ASHPs) are more prevalent than ground-source heat pumps.
As the UK strives to reach Net Zero by 2050, ground source heat pumps are critical to its mission. According to the International Energy Agency, for the UK to reach Net Zero by 2050, there must be no new gas boiler sales after 2025. For this reason, heat pumps are expected to become an increasingly popular choice for home heating.
Pros and Cons of Ground Source Heat Pumps
Pros
Eco-friendly and energy-saving
As a replacement for fossil fuel-based heat and cooling solutions, ground source heat pumps offer more environmental benefits. Without your renewable energy, you’ll likely run your heat pump with grid power, which is often a combination of fossil fuels and renewables. But even if you use non-renewable electricity, ground source heat pumps are highly efficient, so you’re still using less fossil fuel than a boiler. For comparison, heat pumps create 70% fewer carbon dioxide emissions than boilers.
You can expect annual energy savings of £540 if you replace coal systems with heat pumps, according to the Energy Saving Trust. If your current system is LPG and you’re replacing it with a heat pump, you can save up to £1500 per year on your energy bills.
Financial incentives
The UK government offers incentives to encourage people to invest in low-carbon heating solutions. Those eligible for the incentive scheme can save more on heat pumps. For instance, there’s the Boiler Upgrade scheme, where eligible applicants will receive £6,000 for installing a ground source heat pump.
Ground source heat pumps may also reduce your VAT. For those over 60 years old or receiving disability or income support, you might qualify for a 5% tax reduction.
Low maintenance and low running costs
GSHPs will initially cost more than gas boilers. However, they’ll have lower running costs, in the long run, making them a very appealing option as a hot water and heating solution.
There’s also the matter of low maintenance. Although all HVAC systems need routine maintenance, ground source heat pumps contain fewer moving parts than conventional heat pumps. Moreover, geothermal heat pumps have a very long lifespan and last approximately 20 years.
Cons
The relatively high upfront cost
Depending on the system’s size, ground source heat pump installation can be expensive, particularly if you need to upgrade or install ductwork.
Installation can be disruptive
A site survey is required to install your ground loops, followed by some excavation, which can be costly and time-consuming for some homeowners. Installing a ground loop system also requires major aboveground alterations. With a horizontal loop setup, trenching will need to be dug across a large area of your yard, altering its layout and appearance.
Require a lot of space
A ground source heat pump system can take up a fair amount of space on your property. If your home lacks a large enough outdoor space for burying the pipes, the installation of a heat pump can be tricky or not possible. And while ground source heat pumps can be installed in flats, every owner must consent to the expense and disruption involved in installing one.
Ground Source vs. Air Source Heat Pumps
Like GSHPs, air-source heat pumps are more efficient than conventional HVAC systems. However, air-source heat pumps tend to be cheaper than GSHP systems.
What gives GSHPs an edge over ASHPs is that their components are longer-lasting. GSHPs also produce less noise and are largely unaffected by the climate. In contrast, outside temperatures can affect the efficiency of air source heat pumps. However, no matter what type of heat pump you choose to install, both GSHPs and ASHPs can lower your carbon footprint and energy bills in the long term.
Reliable Heat Pump Installation
Need an electrician in Swindon that can install or upgrade your building’s heating and cooling system? At Edmont M&E, our team of experts can help you determine which HVAC system is best for your property. We not only help you install a heat pump in your home or business establishment, but we also offer maintenance services, so they remain in peak condition. Reach out to us today for premium heat pump and boiler services in Swindon.


